Building Decarbonization Resources
Overview & Awareness

Understanding the Sequence and Strategy of Decarbonization
The concept of net-zero is simple: An organization must absorb as much carbon as it emits. Many organizations — and most countries — have committed to net-zero emissions by 2050. This white paper lays out an approach you can take to reduce carbon emissions associated with your facility’s electricity and fuel use and position your organization to capture the benefits of our ever-changing energy landscape between now and then.

FM's New Role: A conduit for collaboration in environmental data
Facility managers have a critical role in the global race to net zero, one which can earn them a well-deserved seat at the corporate table. An FM is the conduit for collaboration between tenants, the property owner and their external business partners to reduce a building’s emissions. It starts with the data, and the information derived from the data empowers decisions.

USGBC Green Building and ESG: What You Need to Know
ESG – or Environmental Social Governance – is everywhere you look these days. What does ESG mean, and why does it matter? Recent current economic, public health, and social justice crises have intensified the already surging interest in ESG. ESG provides a framework to describe governance, business strategy, and expectations. Green building does the work and provides the evidence. Green building is where the rubber meets the road, and companies can demonstrate that they are walking to talk. ESG provides information about organizational governance and management. Stakeholders use this information in their investment decision-making and asset management.

Deloitte’s Sustainability Action Report: Survey Findings on ESG Disclosure and Preparedness
Deloitte commissioned an online of 300 executives at publicly owned companies with a minimum annual revenue requirement of $500 million or more, as well as conducted interviews to increase the total sample size to 100 in each of the following industries: consumer products; financial services; life sciences and health care; oil and gas; and TMT (technology, media and telecommunications). This study finds that Environmental, social, and governance (ESG) concerns continue to ratchet up as stakeholders increasingly expect a company’s business strategy to align with its sustainability commitments, priorities, and requirements. It’s evident that sustainability reporting and disclosure are more than “check-the-box” compliance exercises. ESG is about risk and opportunity. It could underpin your strategy and have the potential to unlock strategic possibilities.

Green Building Provides The Foundation for ESG Reporting in the Property Sector
Green building can provide a credible, defensible foundation for ESG reporting. Green building certification shows that a company is taking specific actions and, increasingly, demonstrating real world performance outcomes. These are not opinions or self-claims. Rather, they are aligned with the values and beliefs of established, publicly available criteria.

Lifecycle GHG Impacts
NBI’s report presents language to incorporate embodied carbon requirements in building codes. Researchers explain the need to address the embodied carbon of the highest emitting materials and the carbon emission benefits for jurisdictions. This report examines the current lack of understanding of what a regulation on embodied carbon would look like in a U.S. base code. The code acknowledges the importance of building materials in the construction industry and aims to achieve practical reductions in climate impact by encouraging lower embodied carbon materials. Example code language can be adopted by jurisdictions starting with product Environmental Product Declarations (EPD) reporting, to target global warming potential (GWP) limits for specific materials, and finally moving to a whole life carbon approach with whole building lifecycle analysis.

How Facility Managers Should Lead Net-Zero Action And How To Start That Journey
The world is now experiencing the convergence of two major crises. The first is the climate crisis, for which most countries are committing to net-zero carbon by 2050. The second is the global energy crisis, with skyrocketing electricity prices having repercussions around the globe.
It’s estimated that up to 50% of today’s buildings will still be in use in 2050, and most of them are wasting up to 30% of the energy they consume. So, it has never been more urgent for building owners and facility managers to retrofit their facilities for more efficient and sustainable operation.
This blog post explains why facility managers need to lead this net-zero effort for their organizations and the steps they should take to ensure success. It will also offer an example of how this proven process delivers tangible results with a fast payback.

US DOE Better Buildings Decarbonization Resource Hub
Explore the many tools, tips and resources gathered by the US Department of Energy to demonstrate real-world emission reduction pathways for all types of buildings and plants. Learn the basics of decarbonization and access tools to start your organization's decarbonization journey.
Decarbonization Guides & Roadmaps

Decarbonization 101: A Six Part Guide
With decarbonization, electrification, energy efficiency, and other ever-changing hot topics being discussed, where can you go for reliable info relevant to your world? Thought leaders share industry insights, innovations, and inspiration on optimizing indoor environments.

Demystifying Decarbonization: A Building Owner and Business Executive Quick Guide
Organizations face challenges to create more efficient operations and achieve sustainability goals. But it doesn't have to be a challenge. Here are 3 steps to successfully decarbonize your building and business.

Decarbonization of the Building Stock and its Operation: The Role of Facility Managers
Decarbonizing building stock and building operations has emerged as a pivotal arena for change. FMs stand at the forefront of this transformation, wielding the potential to significantly impact carbon reduction strategies within the built environment. This report illuminates facility managers’ integral role in steering the built environment toward a sustainable future, analyzing current decarbonization efforts and the operational shifts necessary to meet global climate goals.

A Facility Managers Guide for Net-Zero Buildings
Decarbonizing operations was once revered as “nice to have” but has become a “must do.” As 50% of today’s buildings will still be in use in 2050, it’s not enough to focus on new builds. For building operators, retrofit and refurbishment projects are critical in the journey to decarbonize and must double annually to meet net-zero targets.

US Department of Energy Advanced Energy Design Guide
Achieving Zero Energy series provides a cost-effective approach to achieve advanced levels of energy savings. The guides offer contractors and designers the tools, including recommendations for practical products and off-the-shelf technology, needed for achieving zero energy, which is defined as a building that, on an annual basis, draws from outside resources equal or less energy than it provides using on-site renewable energy sources.

The William J. Worthen Foundation’s Building Decarbonization Practice Guide
The built environment can play a massive role in drawing down greenhouse gas emissions. New buildings and renovations of every type need to be built and operated to zero carbon emission standards. The Building Decarbonization Practice Guide: A Zero Carbon Future for the Built Environment is a tool to accelerate change. A project of the William J. Worthen Foundation, this is an expert-created free compendium of practical, case study-based guidance; an up-to-date reference tool that design professionals (architects, engineers, contractors, and others) as well as developers, funders, and policymakers can apply now.

Insider's Guide to Talking about Carbon Neutral Buildings
The Insider’s Guide to Talking About Carbon Neutral Buildings presents a common language and framework to align market ideas around what it means to design, construct, and operate buildings that contribute little or no carbon emissions. This document explains the relationship between energy and carbon metrics in the built environment and presents the common building components necessary for a carbon neutral future. Each carbon neutral component focuses primarily on building operations and is presented at a high level. The details behind each element can be adjusted to fit specific program needs. The resources within provide more information and support the details.
.png)
Building Electrification Technology Roadmap (BETR)
A guide for developing, implementing, and supporting building electrification & efficiency programs.The roadmap characterizes readiness, product availability, ease of application, market awareness, and greenhouse gas emission reduction potential of 38 key all-electric technologies.

Decarbonization Roadmap Guide for School Building Decision Makers
The Decarbonization Roadmap Guide is written for those interested in healthy, efficient, carbon neutral school design, construction and operation. It outlines achievable goals that result in healthy, affordable, all-electric facilities, and explains common actions taken by leading districts to operationalize their carbon neutral ambitions. Different stakeholders are likely to interact with this framework in different ways, and the guide shares examples of how this can be done. In addition, the guide links to resources and templates that can be customized locally.

Building Performance Standards: A Technical Resource Guide
Building Performance Standards: A Technical Resource Guide is guide is intended to provide technical basis and resources to policymakers, building owners, facility managers, design professionals and ASHRAE members when developing and implementing a Building Performance Standard (BPS).
The guide focuses on larger building types and scope of BPS as developed by leading U.S. cities and states. The guide covers BPS aimed toward reducing building operating energy use and resulting emissions and does not cover embodied energy or carbon, which are addressed by The Whole Life Carbon Guide for Building Systems.

Build it for Zero Carbon: A Roadmap to Realizing Decarbonization of Buildings
Over 120 countries have committed to net-zero 2050 targets. Sustainability is no longer nice to have, it's mandatory in order to remain compliant and competitive. This paper lays out our holistic, replicable strategy for attaining enterprise-level decarbonization targets.

Facility Management And Sustainability: A Fundamental Alliance
This e-book from Planon and Schneider Electric highlights smart, sustainable changes for facility management teams. With these changes, facility management teams can better support their organization's sustainability strategy and bring about positive change within the built environment. It includes use cases and examples of areas where FM teams can be proactive contributors to your organization's sustainability strategy.
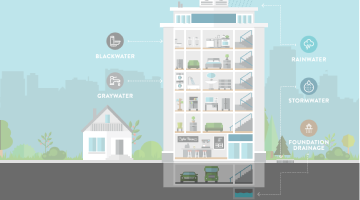
Onsite Non-potable Water Reuse Practice Guide 2.0
The WRPG v2.0 will offer updated practice knowledge that building designers, contractors, owners, operators, and those that regulate this application need to understand, based on lessons from the field since the original Guide’s publication. This update will provide these professionals with information needed to properly scope and integrate onsite water reuse systems into the built environment. While not intended as a design guide, WRPG v2.0 will educate readers about concepts related to water budgets, evaluating project delivery alternatives, and convening a qualified project team. It will empower design professionals to think differently about water and communicate how and why all water is a design resource.

Building Performance Standards
This resource from The Institute for Market Transformation (IMT) focuses on promoting and implementing building performance standards (BPS) to enhance energy efficiency, sustainability, and resilience in construction projects. It provides resources, research, and advocacy efforts to support the adoption of BPS at local, state, and national levels, aiming to drive positive environmental impact and economic benefits in the built environment sector.
Frameworks

Nareit Guide to ESG Reporting Frameworks
With more than a dozen ESG reporting, disclosure, and ranking platforms used by investors, understanding the universe of ESG frameworks is critical to effectively meeting stakeholder expectations. The Guide to ESG Reporting Frameworks provides practical information for REITs about what frameworks exist, how they are used, and what the key differences are between them.

The Big eBook of Sustainability Reporting Frameworks 2022
This eBook is here to guide you through the acronym-laden world of sustainability reporting frameworks by bringing all the key information together in one place.
References & Tools

Low Carbon Technology Strategies Toolkit
This toolkit is designed to support owners and operators of existing buildings in planning retrofit and operational strategies to achieve deep carbon reductions. Low Carbon Technology Strategies are currently available for 10 building types. Recommendations are grouped by technology, with actions categorized as either simple, intermediate, or advanced.

State of the Circular Workplace
A circular workplace is a zero-waste office – but it’s also something much bigger. It’s a growing global movement to bring the principles of the circular economy into the places and spaces where the economy happens. This report brings together building owners, furniture manufacturers, architecture & design firms, and industry associations to offer a 360-degree view of where we are and where we need to go.

US Department of Energy’s Building Energy Data Exchange Specification
The Building Energy Data Exchange Specification (BEDES, pronounced "beads") is a dictionary of terms and definitions commonly used in tools and activities that help stakeholders make energy investment decisions, track building performance, and implement energy-efficient policies and programs. An ecosystem of BEDES-compliant applications will facilitate the exchange of information on building characteristics and energy use.

US Department of Energy’s Building Performance Database
The DOE Building Performance Database (BPD) aspires to build the type of large, aggregate dataset required to analyze drivers of building performance in specific real estate sectors and local markets and understand the relative impacts of different technologies and operational variables.

Getting to Zero Resource Hub
The Getting to Zero Resource Hub is an open-source collection of over 300 zero energy and zero carbon resources across seven different topic areas: design & development, electrification, embodied carbon, local governments toolkit, codes & policy, residential, and schools.

Public Buildings Portfolio Management Initiative
Cities and local governments can lead by example through strategic energy management in municipal facilities. The Public Buildings Portfolio Management Initiative leverages energy benchmarking data and easy-to-use open-source software to organize data, visualize energy usage trends, and uncover high priority opportunities for energy performance improvement across the municipal portfolio.

FirstView Tool
FirstView is a software tool that enables building owners and designers to extract more targeted and useful energy performance information from basic data inputs. The software takes in basic building data and one year’s energy usage and uses multivariable regression analysis to come up with a physical simulation model of the building. The outputs are simple but powerful: we can disaggregate end uses (heating, cooling, electric baseload, and gas/steam baseload), provide diagnostic recommendations for those end-use categories, and compare a building’s energy performance to benchmark values or to previous years’ performance.

Existing Buildings Decarbonization Code
The Existing Building Decarbonization Code is a new way for jurisdictions to reduce carbon emissions and meet Climate Action Plan and public health and equity goals. NBI’s release of the Building Decarbonization Code provided the first off-the-shelf solution--as an overlay to the 2021 International Energy Conservation Code (IECC)--for jurisdictions to transform energy codes into decarbonization codes for new buildings. Expanding where that document left off, the Existing Building Decarbonization Code complements the original adding provisions specifically for existing buildings. The new model language covers both residential and commercial buildings including all-electric and mix-fuel energy use pathways.

Building Decarbonization Code
The Building Decarbonization Code is a groundbreaking tool aiming to deliver carbon neutral performance. The Version 1.2 code language from NBI serves as a building decarbonization overlay to the 2021 International Energy Conservation Code (IECC) and is now compatible with ASHRAE 90.1. The overlay is focused on codes for new construction with the potential of adding code language for existing buildings in a future version. While not an all-electric code, the language does prioritize efficient electric equipment and is designed to be flexible. Sections cover All-Electric and Mixed-Fuel options for residential and commercial construction.

Cost Study of the Building Decarbonization Code
This “Cost Study of the Building Decarbonization Code” analyzes the incremental first cost and life cycle cost of two common building types that follow the code language in NBI’s Building Decarbonization Code. The study, which was supported by the Natural Resources Defense Council (NRDC), analyzes first costs for both all-electric and mixed-fuel paths for single-family and medium office prototypes. It also includes life cycle cost analysis for the single-family scenario. Ultimately, the cost study found that all-electric homes achieve construction savings and mixed-fuel buildings households are only nominally more expensive. It also found marginal additional first costs for property owners of the all-electric medium office building prototype, with most of those attributed to electric vehicle charging infrastructure.

Getting to Zero Buildings Database
NBI works to identify, research, analyze, and promote commercial and multifamily buildings that are leaders in low and zero energy. We maintain the most comprehensive list of zero energy (ZE) commercial and multifamily buildings across North America. This interactive tool puts NBI’s Getting to Zero Buildings Database at your fingertips and allows you to generate customized maps, lists, and charts. Scroll to use the interactive database.

Visualized: How the Power Grid Works
This infographic describes how the US power grid works from energy generation through microgrids, smart technologies, and energy storage. These elements require facility solutions, which will influence future facility managers’ roles.
Visualizing the Flow of Energy-Related CO2 Emissions in the US
This infographic shows US carbon dioxide emissions from energy generation and consumption and the flow of emissions from energy sources to the sectors that use them. Energy-related CO2 emissions refer to the release of carbon dioxide due to the combustion of fuels to produce energy. They arise through the direct use of fossil fuels for transport, heating, or industrial needs, as well as the use of fossil fuels for electricity generation.

The 3 Building Blocks for a Decarbonized Power Sector
This infographic shows the fastest way to net-zero emissions in several sectors, including residential and commercial buildings. In the built environment, this often involves building electrification, energy-efficient lighting, and installing heat pumps as alternatives to oil and gas boilers.

US DOE Building Envelope Campaign
The Building Envelope Campaign is a program designed to help building owners and managers create more energy-efficient buildings. This will be achieved by targeting the building envelope’s thermal performance, determining available energy savings, and providing technical support. Explore resources on their site for a list of commercially available technologies and case studies.

MEASUR – A Free Energy Savings Calculator
MEASUR, a free open-source software tool by Oak Ridge National Laboratory, helps industrial and commercial FMs identify, assess and quantify energy savings and decarbonization opportunities in your operations and energy support systems. With 6 assessment modules and 70+ calculators for motors, pumps, fans, process heating, process cooling and compressed air, it provides quick and simple calculations for fast savings estimates. Globally available, MEASUR includes the ability to switch unit systems and languages, and positively supports energy efficiency and GHG emission reduction efforts worldwide.

Energy Treasure Hunt
"The cheapest energy is the energy you don't use." To discover and reduce sources of wasted energy, you organization should conduct an Energy Treasure Hunt. In this toolkit from the Better Buildings Solutions Center, you can learn how to perform a treasure hunt in your facilities and capture the benefits of reducing energy waste.
Policy & Initiatives

The Impact of Policies, Regulations and Incentives on Decarbonization
Energy plans play a critical role in helping organizations achieve sustainability goals, offset rising energy costs, and optimize a comfortable environment for all.

MEASUR UP: Identifying opportunities in a facility
Learn more about a free, open-source software tool suite: MEASUR (Manufacturing Energy Assessment Software for Utility Reduction). MEASUR helps facility and energy management teams identify, assess, and quantify energy and decarbonization opportunities in their energy intensive systems including motors, pumps, fans, process heating, steam and compressed air. MEASUR also includes a module for energy treasure hunts – organized events to find low-to-no cost savings opportunities. The software is separated into two main categories: calculators and assessment modules. There are more than 70 standalone calculators, most requiring only a few inputs. While quick and simple, these calculators are based on engineering principles and used as a great place to start to find savings or used as reference calculations.

A Climate of Change: Navigating new mandates
For the past few years, facility managers and building operators have increasingly invested in environmental, social and governance (ESG) practices to reach energy efficiency goals. Apart from facilities’ individual endeavors, governments are imposing regulations to get a handle on carbon reduction. With a strategic approach toward energy benchmarking, organizations can confidently build a foundation for complying with mandates, disclosing to stakeholders, managing energy use and contributing to carbon reduction efforts in the long run.

Model Government Zero Emissions Building Policy
The Model Government Zero Emissions Buildings Policy provides plug-and-play policy language for jurisdictions considering taking a “lead by example” approach to building decarbonization. By using their own buildings to demonstrate how new technologies and operational procedures can both reduce energy and carbon emissions, governments can show the market what’s possible.
.png)
Advanced Water Heating Initiative (AWHI)
The national initiative is a coalition of organizations working to make heat pump water heater (HPWH) installations universal in every U.S. home and business. The AWHI is a member-funded collaborative of building owners, utilities, federal agencies, state and local governments, manufacturers, engineers, installers, advocates, researchers, and building industry professionals from across the U.S. that shapes policies, builds demand, brings products to market, and educates the supply chain.

Getting to Zero in Schools Initiative
New Buildings Institute works to transform how American school buildings use energy and contribute to carbon emissions. We partner with state and school district leadership, design professionals, facilities managers, and school occupants to advance districts on the road to carbon neutrality based on our research and learnings in zero energy schools. Schools are positioned to catalyze increased awareness, public support, workforce development, and demand for healthy buildings to help solve the climate crisis. They also serve a central role in addressing equity and enhancing community resilience.

GridOptimal Buildings Initiative
The GridOptimal Initiative created new metrics by which building features and operating characteristics that support more effective building-to-grid operation can be measured and quantified. The initiative provides standards, tools, and guidance to improve building-grid interactions in the built environment by empowering owners, architects, and engineers with dedicated metrics, strategies, and pilot projects. By adopting GridOptimal building features, communities and electric utilities will have a new touchstone to support grid operation. The Initiative is a collaborative effort that includes utilities, regulators, grid operators, building owners, architects, engineers, nonprofits, and others.

Public Buildings Portfolio Management Initiative
Cities and local governments can lead by example through strategic energy management in municipal facilities. The Public Buildings Portfolio Management Initiative leverages energy benchmarking data and easy-to-use open-source software to organize data, visualize energy usage trends, and uncover high priority opportunities for energy performance improvement across the municipal portfolio.

ENERGY STAR NextGen Certification for Commercial Buildings
ENERGY STAR NextGen™ represents the future of ENERGY STAR certification for commercial buildings. It will recognize energy-efficient, low-carbon buildings and will encourage the U.S. building stock to move towards efficient electrification while contributing to the growth of renewable energy.

Node Collective
The NODE Collective is a nonprofit alliance that aims to aggregate and structure comprehensive data on every residential incentive program in the U.S. to support electrification efforts. It focuses on using open data to break down inefficiencies in the current fragmented incentive data landscape, thereby accelerating innovation and market transformation towards decarbonization. The collective comprises a broad coalition of public and private stakeholders and emphasizes open collaboration to enhance the accessibility and usability of incentive data for various users, including consumers, contractors, and businesses.
Forums & Blogs

Why Every Project is a Decarbonization Project
A discussion on how regulations and incentives for decarbonization are impacting customer decisions about which projects to pursue and why controls are included in virtually everyone.

Decarbonizing Health Care Facilities: 3 steps to help chart the path forward
Over the past 25 years, hundreds of health care organizations have partnered with ENERGY STAR to cut costs by reducing energy use, earn recognition by certifying their buildings, and fulfill sustainability goals. Many are leading the field in decarbonization efforts. Hospitals that set ambitious goals now, and back them up with action, will be better prepared for future regulations that might aim to reduce health care sector emissions.

Future Ready Buildings Blog: Increase Asset Value and Reduce Real Estate Investment Risk by Preparing for Building Performance Standards Now
New construction codes have been driving toward net zero performance in jurisdictions around the country but building performance standards (BPS) with similar aims are emerging for existing buildings. Building performance standards are state and local laws that require existing buildings to achieve minimum levels of low-energy or climate-aligned performance. For building owners and operators, BPS means that their properties will have to meet increasingly stringent performance targets for energy and carbon emissions, or risk being identified as poor performers. A future-ready capital planning approach, beginning with long-term performance goals in mind, is an opportunity for building owners to leverage investments and increase asset value while meeting forthcoming BPS.

Next Gen Program
Next Gen is a professional development program of New Buildings Institute for college students, designed to foster the next generation of diverse buildings industry leaders, and in doing so, bolster inclusivity in the buildings industry at large. Over the course of the 9-month program, students will work with each other as part of a Next Gen cohort and have the opportunity for advanced learning, resume building, mentorship, networking and more.

Getting to Zero Forum
The Getting to Zero Forum is the premier event dedicated to building decarbonization. With a growing number of climate emergencies across the United States and around the world, there is no more important time than now for the Getting to Zero Forum. The event brings together the world’s leading experts to share best practice approaches to reducing energy demand and decarbonization related to policy, programs, and projects. It is the only event with a broad cross-section of stakeholders focused on ambitious building efficiency goals and is an ideal venue for organizing both the policy and building communities to achieve zero carbon ambitions.
